anyproxy
A fully configurable proxy in NodeJS, which can handle HTTPS requests perfectly.
Feature
- work as http or https proxy
- fully configurable, you can modify a request at any stage by your own javascript code
- when working as https proxy, it can generate and intercept https requests for any domain without complaint by browser (after you trust its root CA)
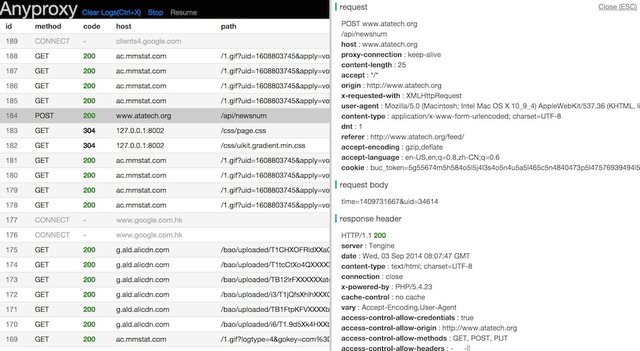
- provide a web interface
Usage
step 1 - install
- install NodeJS
npm install -g anyproxy, may requiresudo
step 2 - start server
- start with default settings :
anyproxy - start with a specific port:
anyproxy --port 8001
step 3 - launch web interface
- visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 with modern browsers
How to write your own rule file
-
with rule file, you can modify a request at any stage, no matter it's just before sending or after servers' responding.
-
actually ruleFile.js is a module for Nodejs, feel free to invoke your own modules.
-
anyproxy --rule /path/to/ruleFile.js -
you may learn how it works by our samples: https://github.com/alipay-ct-wd/anyproxy/tree/master/rule_sample
-
samples in rule_sample
-
rule__blank.js, blank rule file with some comments. You may read this before writing your own rule file.
-
rule_adjust_response_time.js, delay all the response for 1500ms
-
rule_allow_CORS.js, add CORS headers to allow cross-domain ajax request
-
rule_intercept_some_https_requests.js, intercept https requests toward github.com
-
rule_remove_cache_header.js, remove all cache-related headers from server
-
rule_replace_request_option.js, replace request parameters before sending to the server
-
rule_replace_response_data.js, modify response data
-
rule_replace_response_status_code.js, replace server's status code
-
rule_use_local_data.js, map some requests to local file
-
-
rule file scheme is as follows, you may also get it from rule__blank.js
module.exports = {
/*
these functions will overwrite the default ones, write your own when necessary.
*/
//whether to intercept this request by local logic
//if the return value is true, anyproxy will call dealLocalResponse to get response data and will not send request to remote server anymore
shouldUseLocalResponse : function(req,reqBody){
return false;
},
//you may deal the response locally instead of sending it to server
//this function be called when shouldUseLocalResponse returns true
//callback(statusCode,resHeader,responseData)
//e.g. callback(200,{"content-type":"text/html"},"hello world")
dealLocalResponse : function(req,reqBody,callback){
callback(statusCode,resHeader,responseData)
},
//replace the request protocol when sending to the real server
//protocol : "http" or "https"
replaceRequestProtocol:function(req,protocol){
var newProtocol = protocol;
return newProtocol;
},
//req is user's request sent to the proxy server
//option is how the proxy server will send request to the real server. i.e. require("http").request(option,function(){...})
//you may return a customized option to replace the original option
//you should not write content-length header in options, since anyproxy will handle it for you
replaceRequestOption : function(req,option){
var newOption = option;
return newOption;
},
//replace the request body
replaceRequestData: function(req,data){
return data;
},
//replace the statusCode before it's sent to the user
replaceResponseStatusCode: function(req,res,statusCode){
var newStatusCode = statusCode;
return newStatusCode;
},
//replace the httpHeader before it's sent to the user
//Here header == res.headers
replaceResponseHeader: function(req,res,header){
var newHeader = header;
return newHeader;
},
//replace the response from the server before it's sent to the user
//you may return either a Buffer or a string
//serverResData is a Buffer, you may get its content by calling serverResData.toString()
replaceServerResData: function(req,res,serverResData){
return serverResData;
},
//add a pause before sending response to user
pauseBeforeSendingResponse : function(req,res){
var timeInMS = 1; //delay all requests for 1ms
return timeInMS;
},
//should intercept https request, or it will be forwarded to real server
shouldInterceptHttpsReq :function(req){
return false;
}
};
Using https features
step 1 - install openssl
- install openssl ,if you want to use HTTPS-related features. After that, the command
opensslshould be exposed to your shell
step 2 - generate a rootCA and trust it
- you should do this when it is the first time to start anyproxy
- execute
anyproxy --root,follow the instructions on screen - you will see some tip like rootCA generated at : /usr/lib... .
cdto that directory, add/trust the rootCA.crt file to your system keychain. In OSX, you may do that by open the *crt file directly
step 3 - start a https proxy
anyproxy --type https --host my.domain.com- the param
hostis required with https proxy and it should be kept exactly what it it when you config your browser. Otherwise, you may get some warning about security.
Others
work as a module
npm install anyproxy --save
var proxy = require("anyproxy");
!proxy.isRootCAFileExists() && proxy.generateRootCA(); //please manually trust this rootCA
new proxy.proxyServer("http","8001", "localhost" ,"path/to/rule/file.js");
clear all the temperary certificates
anyproxy --clear
Contact
- Please feel free to raise any issue about this project, or give us some advice on this doc. :)