# Getting Start
### install
To Debian and Ubuntu users, you may need to install `nodejs-legacy` at the same time
```bash
sudo apg-get install nodejs-legacy
```
Then install the AnyProxy
```bash
npm install -g anyproxy@beta # 4.x is in beta now
```
### launch
* start AnyProxy in command line, with default port 8001
```bash
anyproxy
```
* now you can use http proxy server by 127.0.0.1:8001
* visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 to see the http requests
### options
* specify the port of http proxy
```bash
anyproxy --port 1080
```
### Use AnyProxy as an npm module
AnyProxy can be used as an npm module
> To enable https feature, please guide users to use `anyproxy-ca` in cli. Or use methods under `AnyProxy.utils.certMgr` to generate certificates.
* install
```bash
npm i anyproxy@beta --save # 4.0 is in beta now
```
* sample
```js
const AnyProxy = require('anyproxy');
const options = {
port: 8001,
rule: require('myRuleModule'),
webInterface: {
enable: true,
webPort: 8002,
wsPort: 8003,
},
throttle: 10000,
forceProxyHttps: false,
silent: false
};
const proxyServer = new AnyProxy.ProxyServer(options);
proxyServer.on('ready', () => { /* */ });
proxyServer.on('error', (e) => { /* */ });
proxyServer.start();
//when finished
proxyServer.close();
```
* Class: AnyProxy.proxyServer
* create a proxy server
```js
const proxy = new AnyProxy.proxyServer(options)
```
* `options`
* `port` {number} required, port number of proxy server
* `rule` {object} your rule module
* `throttle` {number} throttle in kb/s, unlimited for default
* `forceProxyHttps` {boolean} in force intercept all https request, false for default
* `silent` {boolean} if keep silent in console, false for default`false`
* `dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized` {boolean} if ignore certificate error in request, false for default
* `webInterface` {object} config for web interface
* `enable` {boolean} if enable web interface, false for default
* `webPort` {number} port number for web interface
* Event: `ready`
* emit when proxy server is ready
* sample
```js
proxy.on('ready', function() { })
```
* Event: `error`
* emit when error happened inside proxy server
* sample
```js
proxy.on('error', function() { })
```
* Method: `start`
* start proxy server
* sample
```js
proxy.start();
```
* Method: `close`
* close proxy server
* sample
```js
proxy.close();
```
* AnyProxy.utils.systemProxyMgr
* manage the system proxy config. sudo password may be required
* sample
```js
// set 127.0.0.1:8001 as system http server
AnyProxy.utils.systemProxyMgr.enableGlobalProxy('127.0.0.1', '8001');
// disable global proxy server
AnyProxy.utils.systemProxyMgr.disableGlobalProxy();
```
* AnyProxy.utils.certMgr
* Manage certificates of AnyProxy
* `AnyProxy.utils.certMgr.ifRootCAFileExists()`
* detect if AnyProx rootCA exists
* `AnyProxy.utils.certMgr.generateRootCA(callback)`
* generate a rootCA
* Sample
```js
const AnyProxy = require('AnyProxy');
const exec = require('child_process').exec;
if (!AnyProxy.utils.certMgr.ifRootCAFileExists()) {
AnyProxy.utils.certMgr.generateRootCA((error, keyPath) => {
// let users to trust this CA before using proxy
if (!error) {
const certDir = require('path').dirname(keyPath);
console.log('The cert is generated at', certDir);
const isWin = /^win/.test(process.platform);
if (isWin) {
exec('start .', { cwd: certDir });
} else {
exec('open .', { cwd: certDir });
}
} else {
console.error('error when generating rootCA', error);
}
});
}
```
# Proxy Https
* AnyProxy does NOT intercept https requests by default. To view decrypted info, you have to config the CA certificate.
> Under the hood, AnyProxy decryptes https requests by man-in-the-middle attack. Users have to trust the CA cert in advance. Otherwise, client side will issue errors about unsecure network.
* generate certifycates and intercept
```bash
anyproxy-ca #generate root CA. manually trust it after that.
anyproxy --intercept #launch anyproxy and intercept all https traffic
```
* [Appendix:how to trust CA](#config-certification)
# Rule Introduction
AnyProxy provides the ability to load your own rules written in javascript. With rule module, you could customize the logic to handle requests.
> Make sure your rule file is got from a trusted source. Otherwise, you may face some unknown security risk.
Rule module could do the following stuff:
* intercept and modify the request which is being sent
* editable fields include request header, body, target address
* intercept and modify the response from server
* editable fields include response status code, header, body
* intercept https requests, modify request and response
### sample
* Target
* write a rule module to append some text to the response of GET http://httpbin.org/user-agent, and delay the response for 5 seconds
* Step 1,Write the rule file, save as sample.js
```js
// file: sample.js
module.exports = {
summary: 'a rule to modify response',
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url === 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent') {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.body += '-- AnyProxy Hacked! --';
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { // delay
resolve({ response: newResponse });
}, 5000);
});
}
},
};
```
* Step 2, start AnyProxy and load the rule file
* run `anyproxy --rule sample.js`
* Step 3, test
* use curl
```bash
curl http://httpbin.org/user-agent --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
```
* use browser. Point the http proxy of browser to 127.0.0.1:8001, then visit http://httpbin.org/user-agent
* the expected response from proxy is
```
{
"user-agent": "curl/7.43.0"
}
- AnyProxy Hacked!
```
* Step 4, view the request log
* visit http://127.0.0.1:8002, the request just sent should be listed here
### how does it work
* The flow chart is as follows
 * When got an http request, the entire process of proxy server is
* AnyProxy collects all the quest info, include method, header, body
* AnyProxy calls `beforeSendRequest` of the rule module. Rule module deal the request, return new request param or response content
* If `beforeSendRequest` returns the response content, AnyProxy will send the response to client without sending to target server. The process ends here.
* Send request to target server, collect response
* Call `beforeSendResponse` of the rule module. Rule module deal the response data
* Send response to client
* When AnyProxy get https request, it could replace the certificate and decrypt the request data
* AnyProxy calls `beforeDealHttpsRequest` of the rule module
* If the function returns `true`, AnyProxy will do the man-in-the-middle attack to it. Otherwise, the request will not be dealed.
### how to load rule module
* use local file
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./rule.js
```
* use an online rule file
```bash
anyproxy --rule https://sample.com/rule.js
```
* use an npm module
* AnyProxy uses `require()` to load rule module. You could either load a local npm module or a global-installed one.
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./myRulePkg/ #local module
npm i -g myRulePkg && anyproxy --rule myRulePkg #global-installed module
```
# Rule module interface
A typical rule module is as follows. All the functions are optional, just write the part you are interested in.
```js
module.exports = {
// introduction
summary: 'my customized rule for AnyProxy',
// intercept before send request to server
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// deal response before send to client
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) { /* ... */ },
// if deal https request
*beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when dealing requests
*onError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when connect to https server
*onConnectError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ }
};
```
> All functions in your rule file, except summary, are all driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co) . They should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### summary
#### summary
* Introduction of this rule file. AnyProxy will read this field and give some tip to user.
### beforeSendRequest
#### beforeSendRequest(requestDetail)
* Before sending request to server, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* `requestDetail`
* `protocol` {string} the protocol to use, http or https
* `requestOptions` {object} the options of the request-to-go, a param of require('http').request . ref: https://nodejs.org/api/http.html#http_http_request_options_callback
* `requestData` {object} request body
* `url` {string} request url
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `requestDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
protocol: 'http',
url: 'http://anyproxy.io/',
requestOptions: {
hostname: 'anyproxy.io',
port: 80,
path: '/',
method: 'GET',
headers: {
Host: 'anyproxy.io',
'Proxy-Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': '...'
}
},
requestData: '...',
_req: { /* ... */}
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the request protocol,i.e. force use https
```js
return {
protocol: 'https'
};
```
* modify request param
```js
var newOption = Object.assign({}, requestDetail.requestOptions);
newOption.path = '/redirect/to/another/path';
return {
requestOptions: newOption
};
```
* modify request body
```js
return {
requestData: 'my new request data'
// requestOptions can also be used here
};
```
* give response to the client, not sending request any longer. `statusCode` `headers`are required is this situation.
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a or '
}
};
```
### beforeSendResponse
#### beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail)
* Before sending response to client, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendResponse` with param `requestDetail` `responseDetail`
* `requestDetail` is the same param as in `beforeSendRequest`
* `responseDetail`
* `response` {object} the response from server, includes `statusCode` `header` `body`
* `_res` {object} the native node.js response object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `responseDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: {
'Content-Type': 'image/gif',
Connection: 'close',
'Cache-Control': '...'
},
body: '...'
},
_res: { /* ... */ }
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the response status code
```js
var newResponse = Object.assign({}, responseDetail.response);
newResponse.statusCode = 404;
return {
response: newResponse
};
```
* modify the response content
```js
var newResponse = Object.assign({}, responseDetail.response);
newResponse.body += '--from anyproxy--';
return {
response: newResponse
};
```
### beforeDealHttpsRequest
#### beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail)
* When receiving https request, AnyProxy will call `beforeDealHttpsRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* If configed with `forceProxyHttps` in launching, AnyProxy will skip calling this method
* Only by returning true, AnyProxy will try to replace the certificate and intercept the https request.
* `requestDetail`
* `host` {string} the target host to request. Due to the request protocol, full url couldn't be got here
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object. The `_req` here refers to the CONNECT request.
* return value
* `true` or `false`, whether AnyProxy should intercept the https request
### onError
#### onError(requestDetail, error)
* AnyProxy will call this method when an error happened in request handling.
* Errors usually are issued during requesting, e.g. DNS failure, request timeout
* `requestDetail` is the same one as in `beforeSendRequest`
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and AnyProxy will response a default error page
```js
return null;
```
* return a customized error page
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a or '
}
};
```
### onConnectError
#### onConnectError(requestDetail, error)
* AnyProxy will call this method when failed to connect target server in https request
* `requestDetail` is the same one as in `beforeDealHttpsRequest`
* no return value is required
# Rule Samples
* here are some samples about frequently used rule file
* try these samples by `anyproxy --rule http://....js`
* how to test with curl:
* request the server directly `curl http://httpbin.org/`
* request the server via proxy `curl http://httpbin.org/ --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001`
### use local response
* intercept the request towards http://httpbin.org , return the local-defined response
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_use_local_response.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
intercept all requests toward httpbin.org, use a local response
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/user-agent --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
const localResponse = {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: '{"hello": "this is local response"}'
};
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
return {
response: localResponse
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request header
* modify the user-agent sent to httpbin.org
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_header.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify the user-agent in requests toward httpbin.org
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/user-agent --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newRequestOptions.headers['User-Agent'] = 'AnyProxy/0.0.0';
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request body
* modify the post body of http://httpbin.org/post
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_data.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify the post data towards http://httpbin.org/post
test:
curl -H "Content-Type: text/plain" -X POST -d 'original post data' http://httpbin.org/post --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "data": "i-am-anyproxy-modified-post-data" }
*/
module.exports = {
summary: 'Rule to modify request data',
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org/post') === 0) {
return {
requestData: 'i-am-anyproxy-modified-post-data'
};
}
},
};
```
### modify the request target
* send all the request towards http://httpbin.org/ to http://httpbin.org/user-agent
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_path.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
redirect all httpbin.org requests to http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/any-path --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "user-agent": "curl/7.43.0" }
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newRequestOptions.path = '/user-agent';
newRequestOptions.method = 'GET';
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request protocol
* modify the http request towards http://httpbin.org to https
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_protocol.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
redirect all http requests of httpbin.org to https
test:
curl 'http://httpbin.org/get?show_env=1' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "X-Forwarded-Protocol": "https" }
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newOption = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newOption.port = 443;
return {
protocol: 'https',
requestOptions: newOption
};
}
}
};
```
### modify response status code
* modify all status code from http://httpbin.org to 404
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_statuscode.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify all status code of http://httpbin.org/ to 404
test:
curl -I 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.statusCode = 404;
return {
response: newResponse
};
}
}
};
```
### modify the response header
* add X-Proxy-By:AnyProxy to the response header from http://httpbin.org/user-agent
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_header.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify response header of http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl -I 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
X-Proxy-By: AnyProxy
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org/user-agent') === 0) {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.header['X-Proxy-By'] = 'AnyProxy';
return {
response: newResponse
};
}
}
};
```
### modify response data and delay
* append some info to the response of http://httpbin.org/user-agent, then delay the response for 5 seconds.
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_data.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify response data of http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "user-agent": "curl/7.43.0" } -- AnyProxy Hacked! --
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url === 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent') {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.body += '-- AnyProxy Hacked! --';
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { // delay the response for 5s
resolve({ response: newResponse });
}, 5000);
});
}
},
};
```
# Config Certification
### Config root CA in OSX
* this kind of errors is usually caused by untrusted root CA
* When got an http request, the entire process of proxy server is
* AnyProxy collects all the quest info, include method, header, body
* AnyProxy calls `beforeSendRequest` of the rule module. Rule module deal the request, return new request param or response content
* If `beforeSendRequest` returns the response content, AnyProxy will send the response to client without sending to target server. The process ends here.
* Send request to target server, collect response
* Call `beforeSendResponse` of the rule module. Rule module deal the response data
* Send response to client
* When AnyProxy get https request, it could replace the certificate and decrypt the request data
* AnyProxy calls `beforeDealHttpsRequest` of the rule module
* If the function returns `true`, AnyProxy will do the man-in-the-middle attack to it. Otherwise, the request will not be dealed.
### how to load rule module
* use local file
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./rule.js
```
* use an online rule file
```bash
anyproxy --rule https://sample.com/rule.js
```
* use an npm module
* AnyProxy uses `require()` to load rule module. You could either load a local npm module or a global-installed one.
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./myRulePkg/ #local module
npm i -g myRulePkg && anyproxy --rule myRulePkg #global-installed module
```
# Rule module interface
A typical rule module is as follows. All the functions are optional, just write the part you are interested in.
```js
module.exports = {
// introduction
summary: 'my customized rule for AnyProxy',
// intercept before send request to server
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// deal response before send to client
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) { /* ... */ },
// if deal https request
*beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when dealing requests
*onError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when connect to https server
*onConnectError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ }
};
```
> All functions in your rule file, except summary, are all driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co) . They should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### summary
#### summary
* Introduction of this rule file. AnyProxy will read this field and give some tip to user.
### beforeSendRequest
#### beforeSendRequest(requestDetail)
* Before sending request to server, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* `requestDetail`
* `protocol` {string} the protocol to use, http or https
* `requestOptions` {object} the options of the request-to-go, a param of require('http').request . ref: https://nodejs.org/api/http.html#http_http_request_options_callback
* `requestData` {object} request body
* `url` {string} request url
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `requestDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
protocol: 'http',
url: 'http://anyproxy.io/',
requestOptions: {
hostname: 'anyproxy.io',
port: 80,
path: '/',
method: 'GET',
headers: {
Host: 'anyproxy.io',
'Proxy-Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': '...'
}
},
requestData: '...',
_req: { /* ... */}
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the request protocol,i.e. force use https
```js
return {
protocol: 'https'
};
```
* modify request param
```js
var newOption = Object.assign({}, requestDetail.requestOptions);
newOption.path = '/redirect/to/another/path';
return {
requestOptions: newOption
};
```
* modify request body
```js
return {
requestData: 'my new request data'
// requestOptions can also be used here
};
```
* give response to the client, not sending request any longer. `statusCode` `headers`are required is this situation.
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a or '
}
};
```
### beforeSendResponse
#### beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail)
* Before sending response to client, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendResponse` with param `requestDetail` `responseDetail`
* `requestDetail` is the same param as in `beforeSendRequest`
* `responseDetail`
* `response` {object} the response from server, includes `statusCode` `header` `body`
* `_res` {object} the native node.js response object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `responseDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: {
'Content-Type': 'image/gif',
Connection: 'close',
'Cache-Control': '...'
},
body: '...'
},
_res: { /* ... */ }
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the response status code
```js
var newResponse = Object.assign({}, responseDetail.response);
newResponse.statusCode = 404;
return {
response: newResponse
};
```
* modify the response content
```js
var newResponse = Object.assign({}, responseDetail.response);
newResponse.body += '--from anyproxy--';
return {
response: newResponse
};
```
### beforeDealHttpsRequest
#### beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail)
* When receiving https request, AnyProxy will call `beforeDealHttpsRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* If configed with `forceProxyHttps` in launching, AnyProxy will skip calling this method
* Only by returning true, AnyProxy will try to replace the certificate and intercept the https request.
* `requestDetail`
* `host` {string} the target host to request. Due to the request protocol, full url couldn't be got here
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object. The `_req` here refers to the CONNECT request.
* return value
* `true` or `false`, whether AnyProxy should intercept the https request
### onError
#### onError(requestDetail, error)
* AnyProxy will call this method when an error happened in request handling.
* Errors usually are issued during requesting, e.g. DNS failure, request timeout
* `requestDetail` is the same one as in `beforeSendRequest`
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and AnyProxy will response a default error page
```js
return null;
```
* return a customized error page
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a or '
}
};
```
### onConnectError
#### onConnectError(requestDetail, error)
* AnyProxy will call this method when failed to connect target server in https request
* `requestDetail` is the same one as in `beforeDealHttpsRequest`
* no return value is required
# Rule Samples
* here are some samples about frequently used rule file
* try these samples by `anyproxy --rule http://....js`
* how to test with curl:
* request the server directly `curl http://httpbin.org/`
* request the server via proxy `curl http://httpbin.org/ --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001`
### use local response
* intercept the request towards http://httpbin.org , return the local-defined response
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_use_local_response.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
intercept all requests toward httpbin.org, use a local response
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/user-agent --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
const localResponse = {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: '{"hello": "this is local response"}'
};
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
return {
response: localResponse
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request header
* modify the user-agent sent to httpbin.org
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_header.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify the user-agent in requests toward httpbin.org
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/user-agent --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newRequestOptions.headers['User-Agent'] = 'AnyProxy/0.0.0';
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request body
* modify the post body of http://httpbin.org/post
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_data.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify the post data towards http://httpbin.org/post
test:
curl -H "Content-Type: text/plain" -X POST -d 'original post data' http://httpbin.org/post --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "data": "i-am-anyproxy-modified-post-data" }
*/
module.exports = {
summary: 'Rule to modify request data',
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org/post') === 0) {
return {
requestData: 'i-am-anyproxy-modified-post-data'
};
}
},
};
```
### modify the request target
* send all the request towards http://httpbin.org/ to http://httpbin.org/user-agent
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_path.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
redirect all httpbin.org requests to http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl http://httpbin.org/any-path --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "user-agent": "curl/7.43.0" }
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newRequestOptions.path = '/user-agent';
newRequestOptions.method = 'GET';
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
### modify request protocol
* modify the http request towards http://httpbin.org to https
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_request_protocol.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
redirect all http requests of httpbin.org to https
test:
curl 'http://httpbin.org/get?show_env=1' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "X-Forwarded-Protocol": "https" }
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newOption = requestDetail.requestOptions;
newOption.port = 443;
return {
protocol: 'https',
requestOptions: newOption
};
}
}
};
```
### modify response status code
* modify all status code from http://httpbin.org to 404
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_statuscode.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify all status code of http://httpbin.org/ to 404
test:
curl -I 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org') === 0) {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.statusCode = 404;
return {
response: newResponse
};
}
}
};
```
### modify the response header
* add X-Proxy-By:AnyProxy to the response header from http://httpbin.org/user-agent
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_header.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify response header of http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl -I 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
X-Proxy-By: AnyProxy
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('http://httpbin.org/user-agent') === 0) {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.header['X-Proxy-By'] = 'AnyProxy';
return {
response: newResponse
};
}
}
};
```
### modify response data and delay
* append some info to the response of http://httpbin.org/user-agent, then delay the response for 5 seconds.
```bash
anyproxy --rule rule_sample/sample_modify_response_data.js
```
```js
/*
sample:
modify response data of http://httpbin.org/user-agent
test:
curl 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent' --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8001
expected response:
{ "user-agent": "curl/7.43.0" } -- AnyProxy Hacked! --
*/
module.exports = {
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url === 'http://httpbin.org/user-agent') {
const newResponse = responseDetail.response;
newResponse.body += '-- AnyProxy Hacked! --';
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { // delay the response for 5s
resolve({ response: newResponse });
}, 5000);
});
}
},
};
```
# Config Certification
### Config root CA in OSX
* this kind of errors is usually caused by untrusted root CA
 > Warning: please keep your root CA safe since it may influence your system security.
install :
* double click *rootCA.crt*
* add cert into login or system
> Warning: please keep your root CA safe since it may influence your system security.
install :
* double click *rootCA.crt*
* add cert into login or system
 * find the newly imported AnyProxy certificates, configured as **Always Trust**
* find the newly imported AnyProxy certificates, configured as **Always Trust**
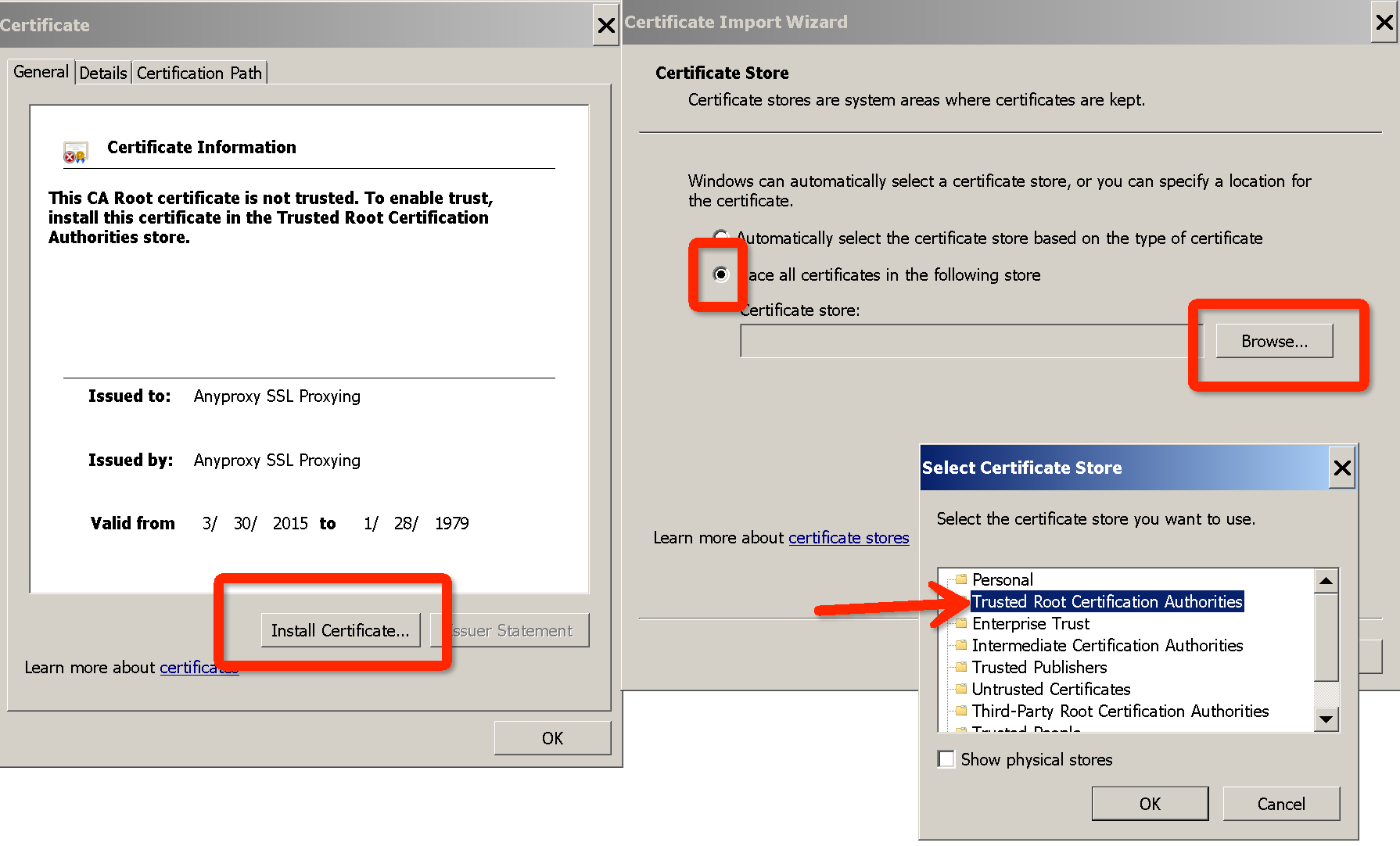
 ### Config root CA in windows
### Config root CA in windows
 ### Config OSX system proxy
* the config is in wifi - advanced
### Config OSX system proxy
* the config is in wifi - advanced
 ### config http proxy server
* take Chrome extent [SwitchyOmega] as an example(https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/padekgcemlokbadohgkifijomclgjgif)为例
### config http proxy server
* take Chrome extent [SwitchyOmega] as an example(https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/padekgcemlokbadohgkifijomclgjgif)为例
 ### trust root CA in iOS
* Click *Root CA* in web ui, and follow the instruction to install
### trust root CA in iOS
* Click *Root CA* in web ui, and follow the instruction to install
 ### trust root CA in iOS after 10.3
* Besides installing root CA, you have to "turn on" the certificate for web manually in *settings - general - about - Certificate Trust Settings*. Otherwire, safari will not trust the root CA generated by AnyProxy.
### trust root CA in iOS after 10.3
* Besides installing root CA, you have to "turn on" the certificate for web manually in *settings - general - about - Certificate Trust Settings*. Otherwire, safari will not trust the root CA generated by AnyProxy.
 ### config iOS/Android proxy server
* proxy settings are placed in wifi setting
* iOS
### config iOS/Android proxy server
* proxy settings are placed in wifi setting
* iOS
 * Android
* Android
 # FAQ
### Q: can not deal https request in rule module.
* A: Any of these options could be used to change the way AnyProxy deall https requests
1. config `--intercept` when luanching AnyProxy via cli, or use `forceProxyHttps` when using as an npm module
2. place a `beforeDealHttpsRequest` function in your rule file and determine which request to intercept by your own.
### Q: get an error says *function is not yieldable*
* A: Rule module is driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co). The functions inside should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### Q: The connection is not private
AnyProxy will propmt this message when the certification of the site you're visiting is not issued by a common known CA. This happens when the certification is self-signed. If you know and trust it, you can ignore the error as below.
- If you run AnyProxy by command line
Pass in the option `--ignore-unauthorized-ssl` to ignore the certification errors, please mind that the option will be active for all connections.
```bash
anyproxy -i --ignore-unauthorized-ssl
```
- If you run AnyProxy by Nodejs
Pass in the option `dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized:true`, like this:
```js
const options = {
...,
dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized: true
};
const anyproxyIns = new AnyProxy.ProxyCore(options);
anyproxyIns.start();
```
*This is also a global option, all certification errors will be ignored*
- With the help of AnyProxy Rule
You can change the request with rule of course. For this scenario, all you need is to pass in an option to Nodejs `Http.rquest`, as we do in AnyProxy. A simple demo below:
```js
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('https://the-site-you-know.com') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
// set rejectUnauthorized as false
newRequestOptions.rejectUnauthorized = false;
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
And we get a bonous here, AnyProxy will only ignore the errors for the site(s) we want it to!
# FAQ
### Q: can not deal https request in rule module.
* A: Any of these options could be used to change the way AnyProxy deall https requests
1. config `--intercept` when luanching AnyProxy via cli, or use `forceProxyHttps` when using as an npm module
2. place a `beforeDealHttpsRequest` function in your rule file and determine which request to intercept by your own.
### Q: get an error says *function is not yieldable*
* A: Rule module is driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co). The functions inside should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### Q: The connection is not private
AnyProxy will propmt this message when the certification of the site you're visiting is not issued by a common known CA. This happens when the certification is self-signed. If you know and trust it, you can ignore the error as below.
- If you run AnyProxy by command line
Pass in the option `--ignore-unauthorized-ssl` to ignore the certification errors, please mind that the option will be active for all connections.
```bash
anyproxy -i --ignore-unauthorized-ssl
```
- If you run AnyProxy by Nodejs
Pass in the option `dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized:true`, like this:
```js
const options = {
...,
dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized: true
};
const anyproxyIns = new AnyProxy.ProxyCore(options);
anyproxyIns.start();
```
*This is also a global option, all certification errors will be ignored*
- With the help of AnyProxy Rule
You can change the request with rule of course. For this scenario, all you need is to pass in an option to Nodejs `Http.rquest`, as we do in AnyProxy. A simple demo below:
```js
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('https://the-site-you-know.com') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
// set rejectUnauthorized as false
newRequestOptions.rejectUnauthorized = false;
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
And we get a bonous here, AnyProxy will only ignore the errors for the site(s) we want it to!
 > Warning: please keep your root CA safe since it may influence your system security.
install :
* double click *rootCA.crt*
* add cert into login or system
> Warning: please keep your root CA safe since it may influence your system security.
install :
* double click *rootCA.crt*
* add cert into login or system
 * find the newly imported AnyProxy certificates, configured as **Always Trust**
* find the newly imported AnyProxy certificates, configured as **Always Trust**
 ### Config root CA in windows
### Config root CA in windows
 ### Config OSX system proxy
* the config is in wifi - advanced
### Config OSX system proxy
* the config is in wifi - advanced
 ### config http proxy server
* take Chrome extent [SwitchyOmega] as an example(https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/padekgcemlokbadohgkifijomclgjgif)为例
### config http proxy server
* take Chrome extent [SwitchyOmega] as an example(https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/padekgcemlokbadohgkifijomclgjgif)为例
 ### trust root CA in iOS
* Click *Root CA* in web ui, and follow the instruction to install
### trust root CA in iOS
* Click *Root CA* in web ui, and follow the instruction to install
 ### trust root CA in iOS after 10.3
* Besides installing root CA, you have to "turn on" the certificate for web manually in *settings - general - about - Certificate Trust Settings*. Otherwire, safari will not trust the root CA generated by AnyProxy.
### trust root CA in iOS after 10.3
* Besides installing root CA, you have to "turn on" the certificate for web manually in *settings - general - about - Certificate Trust Settings*. Otherwire, safari will not trust the root CA generated by AnyProxy.
 ### config iOS/Android proxy server
* proxy settings are placed in wifi setting
* iOS
### config iOS/Android proxy server
* proxy settings are placed in wifi setting
* iOS
 * Android
* Android
 # FAQ
### Q: can not deal https request in rule module.
* A: Any of these options could be used to change the way AnyProxy deall https requests
1. config `--intercept` when luanching AnyProxy via cli, or use `forceProxyHttps` when using as an npm module
2. place a `beforeDealHttpsRequest` function in your rule file and determine which request to intercept by your own.
### Q: get an error says *function is not yieldable*
* A: Rule module is driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co). The functions inside should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### Q: The connection is not private
AnyProxy will propmt this message when the certification of the site you're visiting is not issued by a common known CA. This happens when the certification is self-signed. If you know and trust it, you can ignore the error as below.
- If you run AnyProxy by command line
Pass in the option `--ignore-unauthorized-ssl` to ignore the certification errors, please mind that the option will be active for all connections.
```bash
anyproxy -i --ignore-unauthorized-ssl
```
- If you run AnyProxy by Nodejs
Pass in the option `dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized:true`, like this:
```js
const options = {
...,
dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized: true
};
const anyproxyIns = new AnyProxy.ProxyCore(options);
anyproxyIns.start();
```
*This is also a global option, all certification errors will be ignored*
- With the help of AnyProxy Rule
You can change the request with rule of course. For this scenario, all you need is to pass in an option to Nodejs `Http.rquest`, as we do in AnyProxy. A simple demo below:
```js
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('https://the-site-you-know.com') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
// set rejectUnauthorized as false
newRequestOptions.rejectUnauthorized = false;
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
And we get a bonous here, AnyProxy will only ignore the errors for the site(s) we want it to!
# FAQ
### Q: can not deal https request in rule module.
* A: Any of these options could be used to change the way AnyProxy deall https requests
1. config `--intercept` when luanching AnyProxy via cli, or use `forceProxyHttps` when using as an npm module
2. place a `beforeDealHttpsRequest` function in your rule file and determine which request to intercept by your own.
### Q: get an error says *function is not yieldable*
* A: Rule module is driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co). The functions inside should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### Q: The connection is not private
AnyProxy will propmt this message when the certification of the site you're visiting is not issued by a common known CA. This happens when the certification is self-signed. If you know and trust it, you can ignore the error as below.
- If you run AnyProxy by command line
Pass in the option `--ignore-unauthorized-ssl` to ignore the certification errors, please mind that the option will be active for all connections.
```bash
anyproxy -i --ignore-unauthorized-ssl
```
- If you run AnyProxy by Nodejs
Pass in the option `dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized:true`, like this:
```js
const options = {
...,
dangerouslyIgnoreUnauthorized: true
};
const anyproxyIns = new AnyProxy.ProxyCore(options);
anyproxyIns.start();
```
*This is also a global option, all certification errors will be ignored*
- With the help of AnyProxy Rule
You can change the request with rule of course. For this scenario, all you need is to pass in an option to Nodejs `Http.rquest`, as we do in AnyProxy. A simple demo below:
```js
module.exports = {
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) {
if (requestDetail.url.indexOf('https://the-site-you-know.com') === 0) {
const newRequestOptions = requestDetail.requestOptions;
// set rejectUnauthorized as false
newRequestOptions.rejectUnauthorized = false;
return {
requestOptions: newRequestOptions
};
}
},
};
```
And we get a bonous here, AnyProxy will only ignore the errors for the site(s) we want it to!
 * When got an http request, the entire process of proxy server is
* AnyProxy collects all the quest info, include method, header, body
* AnyProxy calls `beforeSendRequest` of the rule module. Rule module deal the request, return new request param or response content
* If `beforeSendRequest` returns the response content, AnyProxy will send the response to client without sending to target server. The process ends here.
* Send request to target server, collect response
* Call `beforeSendResponse` of the rule module. Rule module deal the response data
* Send response to client
* When AnyProxy get https request, it could replace the certificate and decrypt the request data
* AnyProxy calls `beforeDealHttpsRequest` of the rule module
* If the function returns `true`, AnyProxy will do the man-in-the-middle attack to it. Otherwise, the request will not be dealed.
### how to load rule module
* use local file
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./rule.js
```
* use an online rule file
```bash
anyproxy --rule https://sample.com/rule.js
```
* use an npm module
* AnyProxy uses `require()` to load rule module. You could either load a local npm module or a global-installed one.
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./myRulePkg/ #local module
npm i -g myRulePkg && anyproxy --rule myRulePkg #global-installed module
```
# Rule module interface
A typical rule module is as follows. All the functions are optional, just write the part you are interested in.
```js
module.exports = {
// introduction
summary: 'my customized rule for AnyProxy',
// intercept before send request to server
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// deal response before send to client
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) { /* ... */ },
// if deal https request
*beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when dealing requests
*onError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when connect to https server
*onConnectError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ }
};
```
> All functions in your rule file, except summary, are all driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co) . They should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### summary
#### summary
* Introduction of this rule file. AnyProxy will read this field and give some tip to user.
### beforeSendRequest
#### beforeSendRequest(requestDetail)
* Before sending request to server, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* `requestDetail`
* `protocol` {string} the protocol to use, http or https
* `requestOptions` {object} the options of the request-to-go, a param of require('http').request . ref: https://nodejs.org/api/http.html#http_http_request_options_callback
* `requestData` {object} request body
* `url` {string} request url
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `requestDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
protocol: 'http',
url: 'http://anyproxy.io/',
requestOptions: {
hostname: 'anyproxy.io',
port: 80,
path: '/',
method: 'GET',
headers: {
Host: 'anyproxy.io',
'Proxy-Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': '...'
}
},
requestData: '...',
_req: { /* ... */}
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the request protocol,i.e. force use https
```js
return {
protocol: 'https'
};
```
* modify request param
```js
var newOption = Object.assign({}, requestDetail.requestOptions);
newOption.path = '/redirect/to/another/path';
return {
requestOptions: newOption
};
```
* modify request body
```js
return {
requestData: 'my new request data'
// requestOptions can also be used here
};
```
* give response to the client, not sending request any longer. `statusCode` `headers`are required is this situation.
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a
* When got an http request, the entire process of proxy server is
* AnyProxy collects all the quest info, include method, header, body
* AnyProxy calls `beforeSendRequest` of the rule module. Rule module deal the request, return new request param or response content
* If `beforeSendRequest` returns the response content, AnyProxy will send the response to client without sending to target server. The process ends here.
* Send request to target server, collect response
* Call `beforeSendResponse` of the rule module. Rule module deal the response data
* Send response to client
* When AnyProxy get https request, it could replace the certificate and decrypt the request data
* AnyProxy calls `beforeDealHttpsRequest` of the rule module
* If the function returns `true`, AnyProxy will do the man-in-the-middle attack to it. Otherwise, the request will not be dealed.
### how to load rule module
* use local file
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./rule.js
```
* use an online rule file
```bash
anyproxy --rule https://sample.com/rule.js
```
* use an npm module
* AnyProxy uses `require()` to load rule module. You could either load a local npm module or a global-installed one.
```bash
anyproxy --rule ./myRulePkg/ #local module
npm i -g myRulePkg && anyproxy --rule myRulePkg #global-installed module
```
# Rule module interface
A typical rule module is as follows. All the functions are optional, just write the part you are interested in.
```js
module.exports = {
// introduction
summary: 'my customized rule for AnyProxy',
// intercept before send request to server
*beforeSendRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// deal response before send to client
*beforeSendResponse(requestDetail, responseDetail) { /* ... */ },
// if deal https request
*beforeDealHttpsRequest(requestDetail) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when dealing requests
*onError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ },
// error happened when connect to https server
*onConnectError(requestDetail, error) { /* ... */ }
};
```
> All functions in your rule file, except summary, are all driven by [co](https://www.npmjs.com/package/co) . They should be yieldable, i.e. return a promise or be a generator function.
### summary
#### summary
* Introduction of this rule file. AnyProxy will read this field and give some tip to user.
### beforeSendRequest
#### beforeSendRequest(requestDetail)
* Before sending request to server, AnyProxy will call `beforeSendRequest` with param `requestDetail`
* `requestDetail`
* `protocol` {string} the protocol to use, http or https
* `requestOptions` {object} the options of the request-to-go, a param of require('http').request . ref: https://nodejs.org/api/http.html#http_http_request_options_callback
* `requestData` {object} request body
* `url` {string} request url
* `_req` {object} the native node.js request object
* e.g. When requesting *anyproxy.io*, `requestDetail` is something like the following
```js
{
protocol: 'http',
url: 'http://anyproxy.io/',
requestOptions: {
hostname: 'anyproxy.io',
port: 80,
path: '/',
method: 'GET',
headers: {
Host: 'anyproxy.io',
'Proxy-Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': '...'
}
},
requestData: '...',
_req: { /* ... */}
}
```
* Any of these return values are valid
* do nothing, and return null
```js
return null;
```
* modify the request protocol,i.e. force use https
```js
return {
protocol: 'https'
};
```
* modify request param
```js
var newOption = Object.assign({}, requestDetail.requestOptions);
newOption.path = '/redirect/to/another/path';
return {
requestOptions: newOption
};
```
* modify request body
```js
return {
requestData: 'my new request data'
// requestOptions can also be used here
};
```
* give response to the client, not sending request any longer. `statusCode` `headers`are required is this situation.
```js
return {
response: {
statusCode: 200,
header: { 'content-type': 'text/html' },
body: 'this could be a